Hydroponic vs Aquaponic – Which One Is Better?

This post follows our research editorial guidelines.

The compact nature and reliable harvests of hydroponic herb or vegetable gardening is hard to beat. It’s often the best way to ensure a regular supply of healthy and delicious herbs and veggies even in the heart of winter. But what about protein? Aquaponics is an approach that brings lean meat in the form of fish to the table alongside crisp greens and flavorful hydroponic herbs.
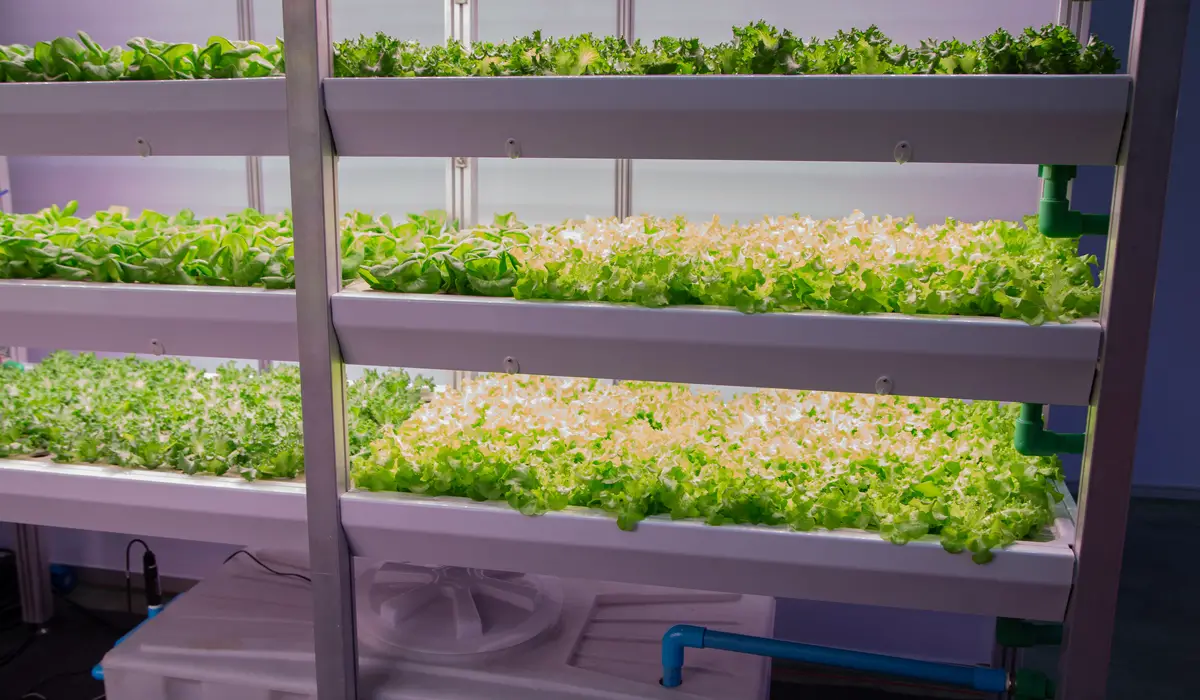

Table of Contents
What Is The Difference Between Hydroponics And Aquaponics?
Aquaponic systems incorporate live fish. The waste from their droppings fertilizes plants, and plants filter water for the fish. Fish can be later harvested for food.
What is Hydroponic gardening?
I’m a longtime fan of hydroponics and what it can do for growers worldwide. Hydroponic cultivation is a system that uses water instead of soil to grow crops. Most systems involve pumps and filters to keep the water moving through the roots, and techniques to keep the liquid rich in oxygen.
Comparison chart: Aquaponic vs Hydroponics
| Comparison | Aquaponics | Hydroponics |
| Complexity to setup | High | Low |
| Cost to maintain | Low to Moderate | Variable |
| Cost to setup | High | Variable |
| Expected yield | High | Variable |
| Environmental impact | Low | Low |
| Nutrients Needed | Low | High |
| PH Range | 6.0-9.0 | 5.5-6.0 |
Advantages of hydroponic growing
Easy
Hydroponic growing is far simpler than it looks. So long as you keep roots wet and well fed, and the leaves in good light, you’ll get crops.
Beginners can start with self-contained systems like the AeroGarden that are no more difficult to use than a microwave. Put solution in, press a button and voila! You’re off and running.
Once you have the hang of simple plants like hydroponic lettuce, it’s not much of a stretch to move on to trickier crops like peppers or broccoli. It’s not a steep learning curve and a very rewarding one, too.
Adaptable
Home hydroponics is versatile and well suited to just about every grower. They can be as complex or as simple as your needs and budget require.
If you’re in a warm climate, a salad table style deep water setup on a sunny porch can deliver lush salads for very little outlay. If you’re in the north as I am, compact indoor rigs with grow lights provides year-round fresh vegetables even as snow falls outside.
Compact
You don’t need much space for home hydroponics. There’s a lot of space-saving commercial kits on the market, with a style to suit most growers.
It’s also not hard to build around the limitations of your space. Apartment dwellers can go up a wall with a vertical garden. High shelves over work-spaces are perfect to run a nutrient film channel. And any system with a grow light can transform a gloomy basement into a verdant wonderland.
Cheap
Hydroponic systems are easy to build from common household items like buckets, plastic storage containers, discarded gutters and the like. The bar for entry is very low indeed. If you want to start small, you can spend small, too.
3 Disadvantages of hydroponic growing
Does not supply protein
Leafy vegetables and herbs are not enough to keep a body going by themselves. If you want to provide a balanced diet you need protein. Growing enough protein rich foods like beans and lentils in a hydroponic setup is a challenge for the home grower.
Requires synthetic inputs
Hydroponic growing requires constant input. Due to the high density of the plantings it’s also important to be precise and as free from disease causing bacteria or fungi as possible.
Organic fertilizers tend to be lower in nutrient value, and they lack precision. They also present a substantial contamination risk. Manures and composts are vibrant communities of micro-organisms that can cause real problems for hydroponic setups. You’ll need to stick to synthetics.
Requires Constant Fertilization
By definition hydroponics grow plants in sterile media. There’s no dirt involved and without dirt there’s no naturally occurring fertility. You have to keep adding more and more fertilizer as your crops mature. Managing nutrients is the single biggest part of hydroponics.
It’s very easy to wind up with deficiencies even if you do fertilize regular. You need to monitor your solution daily.
Which plants grow well in a Hydroponic setup

Leafy crops of all types grow well in hydroponic setups. Lettuces, spinach, cabbages and silverbeet are classic crops for home growers.
Nightshades like tomatoes, peppers and eggplants also thrive in hydroponic setups. They can be fussy and so respond well to the hands-on approach that hydroponics requires.
Finally leafy herbs like basil, parsley and oregano are also great choices for home hydroponic systems. It’s pure magic to clip fresh herbs just seconds before you cook with them.
What is the Aquaponic Method?
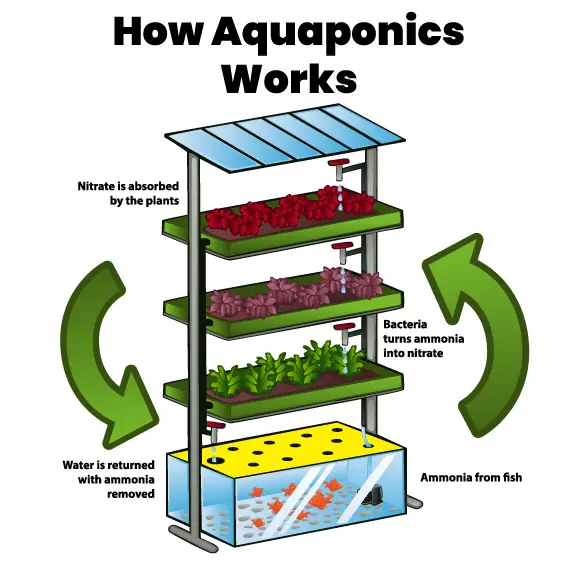
Aquaponics is similar to hydroponics in many regards. Both use water to transmit nutrients to the root systems of plants. Both often use filters, aeration, and grow lights to boost productivity.
The key difference is how that water is used. In aquaponics, fish swim through the tank of water that feeds the plants. Their waste is broken down by friendly bacteria into fertilizer for the plants. The plants in turn help filter the water, keeping it clean and fresh for the fish.
“Aquaponics is a method of growing fish and plants in a closed water system. Fish waste provides the plants’ nutrients, while the plants purify the water to help keep the fish healthy. An aquaponics system has separate fish and plant components that contribute to the overall benefit of this productive system.”
Lance Beecher, Assistant Extension Specialist, Fisheries, Aquaculture, and Aquaponics, Clemson University
Advantages of Aquaponic Growing
Complete Meals
Imagine the satisfaction of a roast fish supper with fresh greens and dill dressing, all grown yourself. It’s a fantastic way to get the absolute most from a single system. If you’re keen on taking control of where you food comes from it’s hard to beat.
Profitable
If you’re keen to make a bit of money on the side, aquaponics gives you multiple products to sell. Get your inputs right and choose a good fish for your market, and you can really make a bit of money. Depending on the species, fish can reach a sellable size in around six or seven months. Choose your fish wisely and you may well find the system pays for itself.
Fewer Chemicals
Fish eat just about anything. They’ll devour fish pellets made from easy to get material and turn it to rich nutrients for the plants above. Unlike liquid fertilizers their food requires very little processing, and is often made from the same basics we eat – wheat, soy, corn and other such things.
Using fish waste to fertilize your plants cuts back the amount of synthetics needed by the system. You might need to add macros like boron or magnesium, but in general it dramatically reduces what you have to add.
3 Disadvantages of Aquaponic growing
Larger space requirements
Fish need space to thrive. Depending on the species you choose this may require a substantial footprint for your system. If you don’t give them the right space they’ll suffer and you’ll get less fish to eat and poorer support for the plants.
In addition to the tank that houses them, fish also need filters, aeration equipment and temperature control. You also need to make space for bags of food. It needs as much kit as a large aquarium, with the extra space needed for a hydro rig too!

More Complex
Aquaponics combines the complexity of hydroponics with the complexity of aquaculture. It’s two systems with their own needs, and while a lot of those needs overlap and help create a single stable growing environment, it’s a lot of work to maintain.
It’s double the learning and double the involvement. I know they’re some of you rubbing your paws together in delight at the prospect of learning two new wonderful skills, but it’s a lot to take on for most people.
Requires Electricity
It’s entirely possible to run a hydroponic setup with little to no electricity at all. If you have a well lit balcony or a room with the right aspect, you can grow in natural light. Passive systems also need no power for circulation or aeration too.
That changes once you add fish to the mix. They need filters and aeration or they won’t survive. If you’re in a cool climate you’ll have to heat their water, too. An aquaponics rig is effectively chained to its power outlet.
More Expensive
An indoor hydroponic garden doesn’t need to be a big investment. A Kratky setup is literally just a bucket with a hole in the lid and a bit of fertilizer. They can be astonishingly cheap and provide a rich bounty from very little investment.
This is not the case with aquaponics. You can’t cheap out on your fish or they simply up and die. A canny grower can make their own tanks and plant beds from recycled or repurposed materials, but beginners are going to have to spend up to get a system that is fruitful.
Which plants grow well in a Aquaponic setup
Many of the same plants that do well in hydroponics do well in aquaponics. It makes it easy for experienced hydro growers to try something new and branch out into aquaponics.
Leafy greens and herbs in particular thrive. More nutrient intensive plants like peppers and tomatoes are also options, but they require a higher density of fish. It’s best to keep them in hydro as a rule.
Is Aquaponic more expensive than hydroponic growing?
When it comes to cost it pays to consider aquaponics as a double system. You’re paying for an aquarium setup that pairs with a hydroponic garden. This is especially true if you have the skills to knock a hydro rig together yourself.
But that investment does pay dividends. It results in lower fertilizer inputs, and if you plan on eating your fish you’ll definitely notice the payoff. It’s also possible to produce systems that result in zero net costs by selling your fish and vegetables to neighbors or friends.
Do plants grow faster in Aquaponic or Hydroponic systems?
The largest factors to speed of growth is light and temperature. You can nourish your garden abundantly, but if it’s cold and dark your growth will slow. No amount of fish poop or factory fertilizer will change that.
Does Aquaponic systems increase yield?
Tradition hydroponics generally produce more plants. The grower can tailor the nutrient solution to any individual plant to ensure spectacular growth. This is especially true of heavy feeders like broccoli, tomatoes and the like. Other crops, like basil, really don’t have much difference at all.
The big difference is you get fish in addition to vegetables when you use aquaponics. How you divide your space and efforts will decide how much of the yield is seafood and how much is what you eat on the side.
Is hydroponics or aquaponics more profitable in farming?
Profitability in farming is a tricky subject. A lot depends on what’s going on in local markets. For example freshwater fish grown in the middle of an arid area will turn a profit far more than the same fish grown somewhere close to active fisheries. It can make it a bit of work choosing what crops and what fish to grow. It’s also labor intensive, with a full third of the production costs coming from paying workers to tend to fish and plants. It’s a lot to consider.
The biggest markets for aquaponics is in cities and build up areas far from fisheries. It’s also a fantastic choice in terms of our carbon footprint. A fish grown in a warehouse around the corner from the people who eat it will be fresher, more delicious and spend less time being shipped than one from far away.
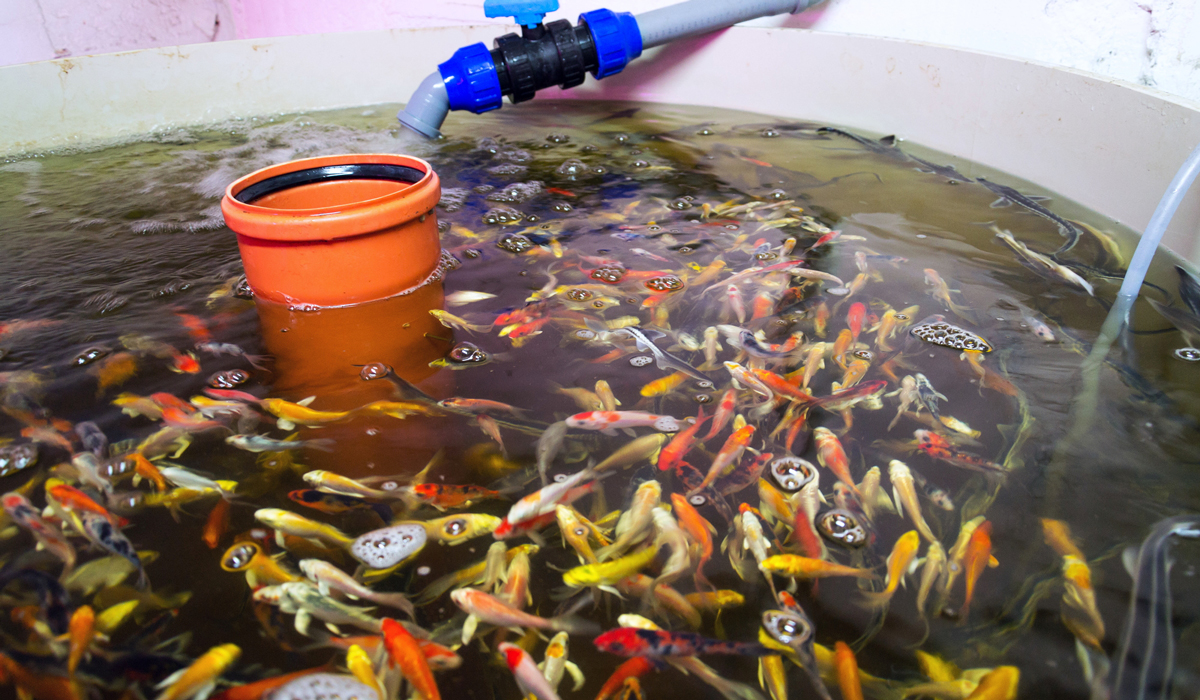
Which fish are best to use in Aquaponic setups
Fish for aquaponics must be freshwater fish that grow quickly and do a good job converting their feed into body weight and fertilizer.
Tilapia are the gold standard for aquaponics. They grow quickly and are large enough to eat or sell in as little as seven months. Other food fish grown in aquaponics include catfish, bass and even freshwater prawns.
Ornamental fish also work just fine in home aquaponics setups. If you’re not planning on eating them, koi are garbage guts that will eat just about anything and turn it very efficiently into fertilizer. Even goldfish will get the job done.
Final thoughts
I don’t compare apples to oranges, and it’s likewise tough to compare aquaponics to hydroponics. I’ll be sticking to hydroponics for the future thanks to its versatility, especially since fantastic fish is available close to me. But aquaponics is an intriguing next step for those of you who want to take a bit more control of their food.

Before you go!
How To Grow The Best Hydroponic Tomatoes: From Seed to Savory
How to Choose a Hydroponic Grow Sponge + Which Ones You Should Avoid…
The Kratky method: A Passive Hydroponic way to grow plants
Hydroponics vs. Aeroponics: Which one Reigns Supreme?